Go to Page 1 (What is NB?/ Risk Stratification), Home
3. Histologic Evaluation of
Neuroblastoma
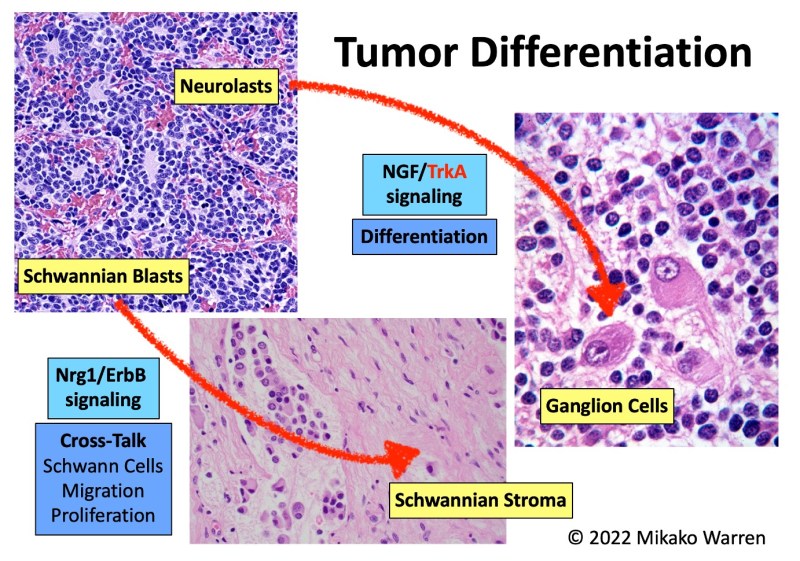
- PNT comprises two histologic cell types.
- Neuroblastic tumor cells
- Schwann cells and Schwannian stroma – induced by the neuroblastic cells during differentiation
- Divided into histologic subtypes depending on the degrees of:
- Differentiation and maturation of neuroblastic cells (tumor cells)
- Schwann cells/Schwannian stroma
International Neuroblastoma Pathology Classification (INPC) of Peripheral Neuroblastic Tumors

- Histologic evaluation of PNT Based on “International Neuroblastoma Pathology Classification (INPC)”
- Neuroblastoma (NB) – Schwannian stroma-poor
- Undifferentiated NB
- Poorly differentiated NB
- Differentiating NB
- Ganglioneuroblastoma (GNB) – Schwannian stroma-rich
- Intermixed GNB
- Nodular GNB
- Ganglioneuroma (GN) – Schwannian stroma-dominant
- Maturing GN
- Mature GN
- Neuroblastoma (NB) – Schwannian stroma-poor

1. Neuroblastoma (NB) Subtype
- Neuroblastoma (NB, Schwannian stroma-poor form, <50% of the tumor volume
- Further divided into three groups based on the degrees of neuroblastic cell differentiation.
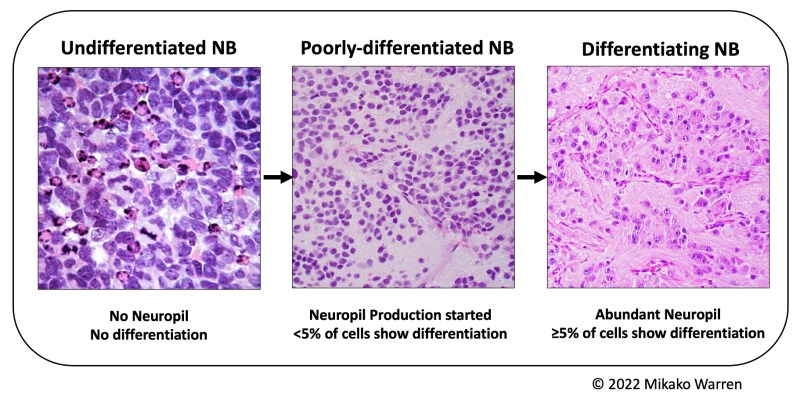
- Undifferentiated NB (UD-NB)
- Undifferentiated small round blue neuroblastic cells
- No neuropil production
- Poorly differentiated NB (PD-NB):
- Mildly differentiated neuroblastic cells (<5% of tumor cells)
- Neuropil production present
- Differentiating NB (D-NB):
- ≥5% differentiated neuroblastic cells
- Neuropil production present
- Undifferentiated NB (UD-NB)
- MKI is applied to only NB.
Mitosis-Karyorrhexis Index (MKI)

- Only used for NB (including NB component in GNB nodular)
- Count 5000 cells!!
- Take an average from multiple areas
- Low: <100/5000 cells (<2%)
- Intermediate: 100-200/5000 cells (2-4%)
- High: ≥200/5000 cells (≥4%)
2. Ganglioneuroblastoma (GNB) subtype
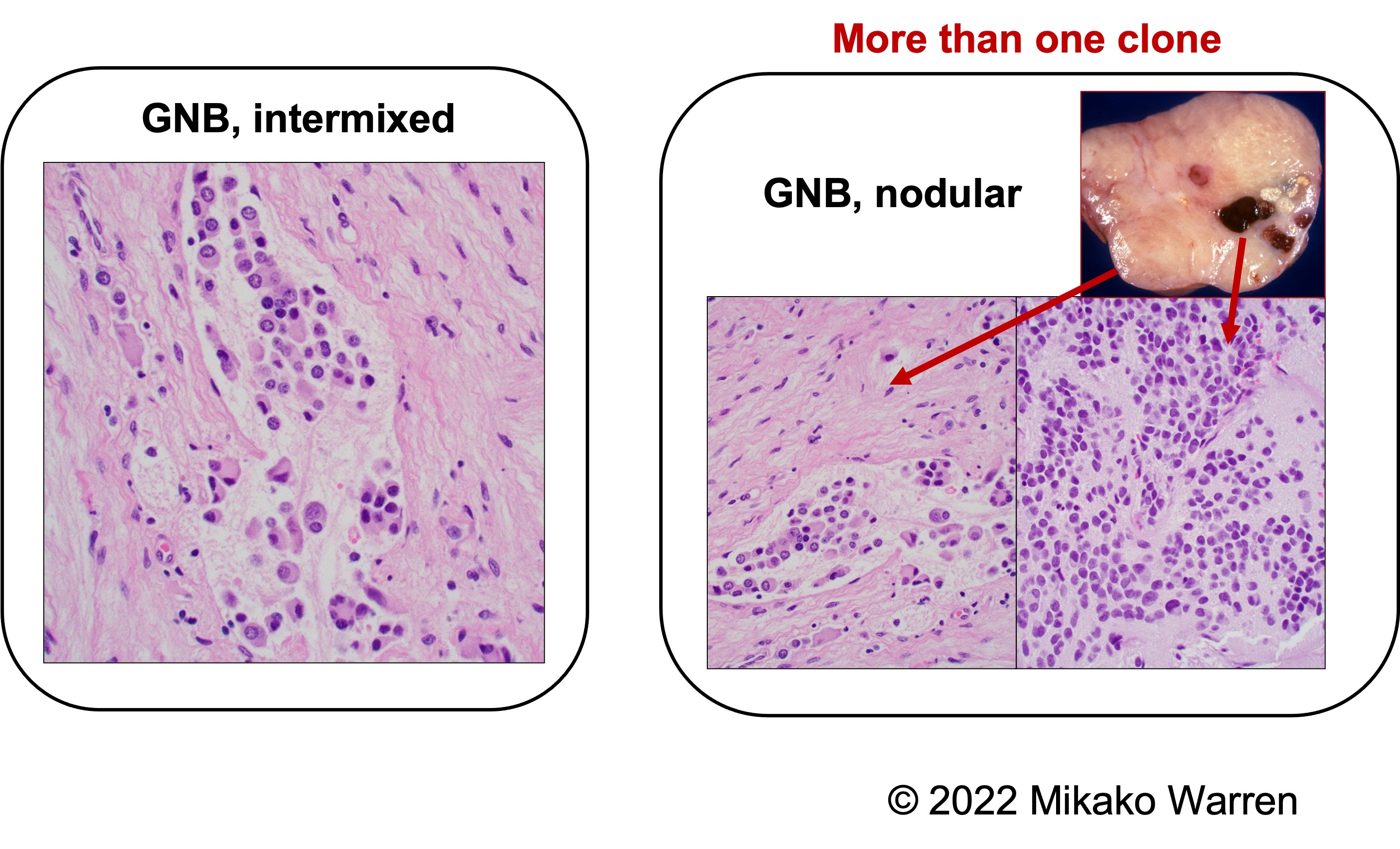
- Ganglioneuroblastoma, intermixed (GNB, Schwannian stroma-rich form, ≥50%)
- Islands of neuroblastic cells + neuropil
- Abundant Schwannian-stroma background
- Nodular GNB is a form of GNB.
- More than one clone with a Schwannian stroma-poor (NB) component and rich/predominant (GNB/GN) component.
3. Ganglioneuroma (GN) subtype

- Ganglioneuroma (GN, Schwannian stroma-dominant form, of course ≥50%)
- The most mature subtype with:
- Maturing/matured neuroblastic cells = ganglion cells
- Neuropil production is no longer identified.
Favorable and Unfavorable Histology
- Favorable histology (FH) – age-appropriate differentiation
- Unfavorable histology (UH) – not appropriately differentiated for age


